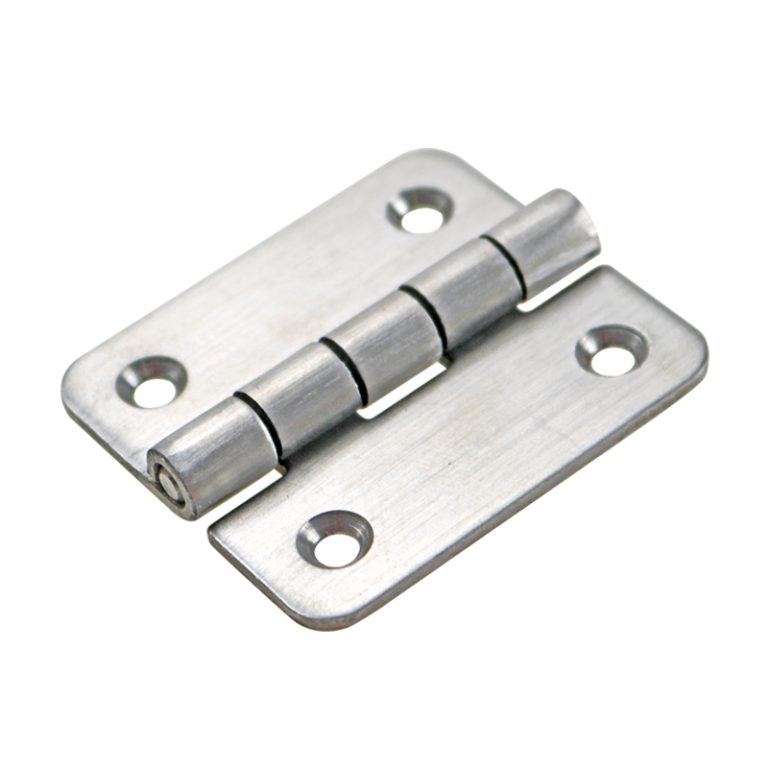
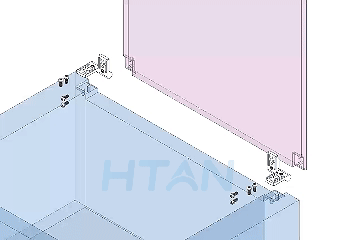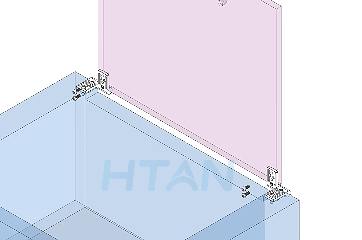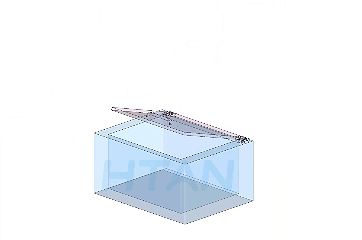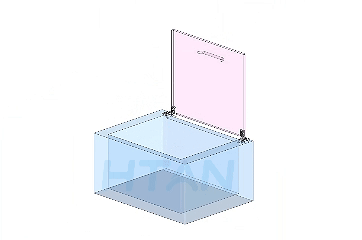
HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

Heavy-duty hinges are hardware components specifically designed for high-load and high-frequency door operation scenarios. Their primary function is to support and stabilize the connection between cabinet doors and enclosures. Compared to standard hinges, heavy-duty hinges use stronger materials (such as stainless steel, zinc alloy, or cold-rolled steel) and reinforced structures (such as bearing-type or continuous hinges), making them capable of handling greater weight and more complex mechanical stresses.
In industrial applications, heavy-duty hinges are commonly found in electrical cabinets, server room doors, and cold storage doors. Their design must consider rust resistance, corrosion resistance, and impact resistance to withstand high temperatures, humidity, and frequent usage.
1.The Importance of Heavy-Duty Hinges
2.Load-Bearing Requirements
3.Safety Protection
4.Durability
5.Core Functions of Heavy-Duty Hinges
5.1.Load-Bearing and Stability
5.2.Environmental Resistance
5.3.Safety and Quiet Operation
6.How to Choose the Right Heavy-Duty Hinge
6.1.Selecting the Right Type Based on Application
6.2.Key Selection Criteria
6.3.Compatibility Testing
7.Recommended Model: HTAN HT072-1
7.1.Application Areas
7.2.Common Issues and Solutions
8.Installation and Maintenance Guide
8.1.Installation Steps
8.2.Common Installation Mistakes
8.3.Maintenance Tips
Conclusion
1.The Importance of Heavy-Duty Hinges
The stability and safety of equipment cabinet doors directly depend on the performance of hinges. The key benefits of heavy-duty hinges include:
2.Load-Bearing Requirements
Industrial electrical cabinets or equipment doors are typically made of metal or composite materials, which are relatively heavy. Standard hinges often fail to support the weight, causing door sagging or deformation. Heavy-duty hinges, through optimized structural design (such as multi-stage bearings), distribute pressure evenly and extend the lifespan of cabinets.
3.Safety Protection
In high-voltage electrical cabinets or explosion-proof equipment, a cabinet door failure due to hinge malfunction could lead to serious accidents. Heavy-duty hinges strengthen connection points, support limiters, or integrate safety lock designs to enhance protection levels.
4.Durability
In industrial environments where cabinet doors undergo frequent opening and closing, standard hinges tend to wear out or rust. Heavy-duty hinges feature surface coatings (such as matte or polished finishes) and wear-resistant materials (such as zinc alloy), significantly reducing maintenance frequency.
5.Core Functions of Heavy-Duty Hinges
5.1.Load-Bearing and Stability
By reinforcing the hinge pin and leaf structure, heavy-duty hinges can support doors weighing hundreds of kilograms. For example, electrical cabinet hinges made from #4 zinc alloy offer high tensile strength, ensuring precise alignment between the cabinet door and the enclosure even after long-term use.
5.2.Environmental Resistance
For outdoor or humid environments, stainless steel or galvanized steel materials effectively prevent rust. In high-temperature workshops, heat-resistant coatings prevent hinge failure due to thermal expansion.
5.3.Safety and Quiet Operation
Some heavy-duty hinges incorporate hydraulic damping technology to enable slow door closure, preventing hand injuries and reducing noise. For instance, damping hinges utilize liquid buffering mechanisms to extend closure times to 4–6 seconds, improving operational safety.
6.How to Choose the Right Heavy-Duty Hinge
6.1.Selecting the Right Type Based on Application
- Industrial Electrical Cabinets: Require waterproof and dustproof continuous hinges, preferably made of zinc alloy with a matte finish to match industrial equipment aesthetics.
- Medical and Cleanroom Equipment: Stainless steel hinges that are easy to clean and prevent dust accumulation.
6.2.Key Selection Criteria
- Load Capacity: Choose hinges based on the cabinet door weight (e.g., 20kg to over 100kg).
- Opening Angle: Standard hinges open at 90°, but for specific needs (such as equipment maintenance), 165° wide-angle hinges may be required.
6.3.Compatibility Testing
Before installation, confirm hinge compatibility with cabinet thickness and screw hole alignment. If necessary, use anti-loosening nuts or washers for added stability.
7.Recommended Model: HTAN HT072-1
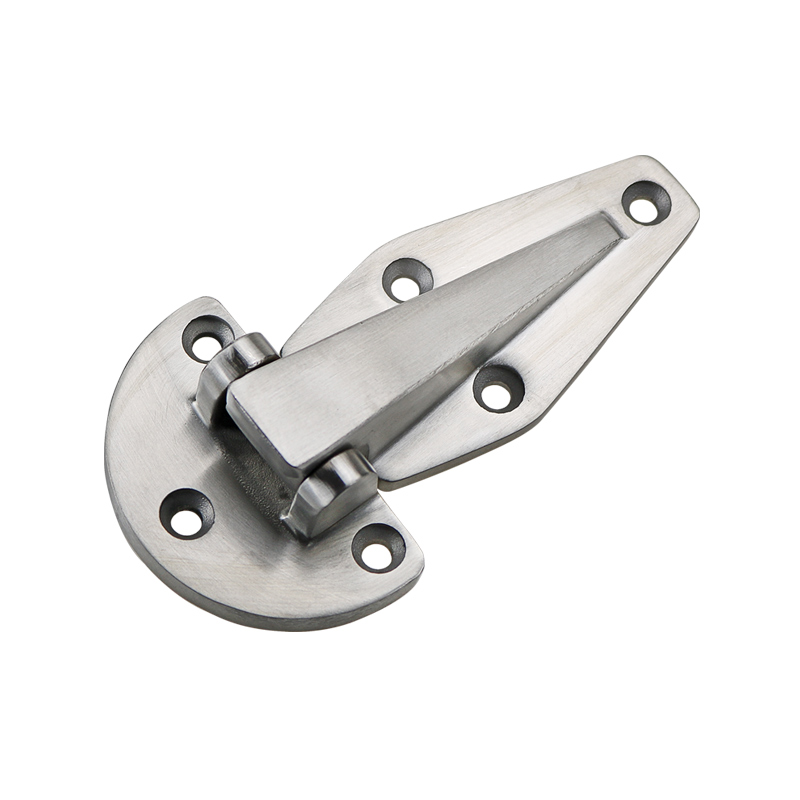

The HT072-1 industrial oven door hinge is made of stainless steel with a brushed surface, measuring 150mm × 80mm. It is suitable for industrial ovens, cold storage doors, and steam cabinet doors. We accept OEM orders with customization options for size, color, material, and finish.
7.1.Application Areas
- Baking Equipment: Crucial for bread ovens, biscuit ovens, and similar devices.
- Large Warehouse Shelving and Cabinet Doors: Used in logistics warehouses for tool, equipment, or valuable item storage.
- Industrial Refrigerators and Freezers: Withstand weight and internal-external pressure variations caused by temperature differences.
- Heavy Machinery Control Cabinets: Found in mining equipment, construction machinery, and other large-scale machinery control enclosures.
7.2.Common Issues and Solutions
1.Industrial Oven Door Hinges Warping Under High Temperatures
Solution: Ensure hinges are made from heat-resistant stainless steel. If slight warping occurs, adjust installation screws and realign the cabinet door.
2.Poor Sealing of Industrial Oven Hinges Leading to Heat Loss
Solution: Install high-temperature-resistant sealing materials, such as silicone strips. Also, inspect the hinge structure for damage and replace faulty components.
3.Hinges Rusting Quickly
Solution: For minor rusting, gently sand the surface and wipe clean before applying high-temperature rust-proof oil.
4.Hinges Loosening After Frequent Use
Solution: Use appropriate tools (such as screwdrivers) to tighten screws. If screw holes are worn out, use larger screws or a thread repair kit.
5.Determining Hinge Load Capacity
Solution: Calculate the door’s total weight, including its material and any attached accessories. Refer to the product manual for hinge weight capacity ratings.
8.Installation and Maintenance Guide
8.1.Installation Steps
- Positioning and Measurement: Evenly distribute hinges along the cabinet door height (typically 2–3 hinges per door). Top and bottom hinges should bear most of the weight.
- Securing and Adjusting: Use a power drill for precise hole placement. Fully tighten screws, then test door movement and adjust hinge tension as needed.
8.2.Common Installation Mistakes
- Insufficient Hinges: Too few hinges lead to uneven stress distribution, accelerating wear.
- Material Mismatch: Using non-rust-proof hinges in humid environments can cause premature failure.
8.3.Maintenance Tips
- Regularly clean hinge surfaces to remove oil and dust, applying lubricating grease to minimize friction.
- Check screw tightness and promptly replace worn-out bearings or deformed hinges.
Conclusion
While heavy-duty hinges may seem like small components, they are critical for cabinet door safety and functionality. From selection to installation, factors such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance must be considered. As industrial automation and environmental regulations evolve, material innovation and functional integration will continue to drive advancements in heavy-duty hinge technology, providing more efficient solutions for equipment protection.