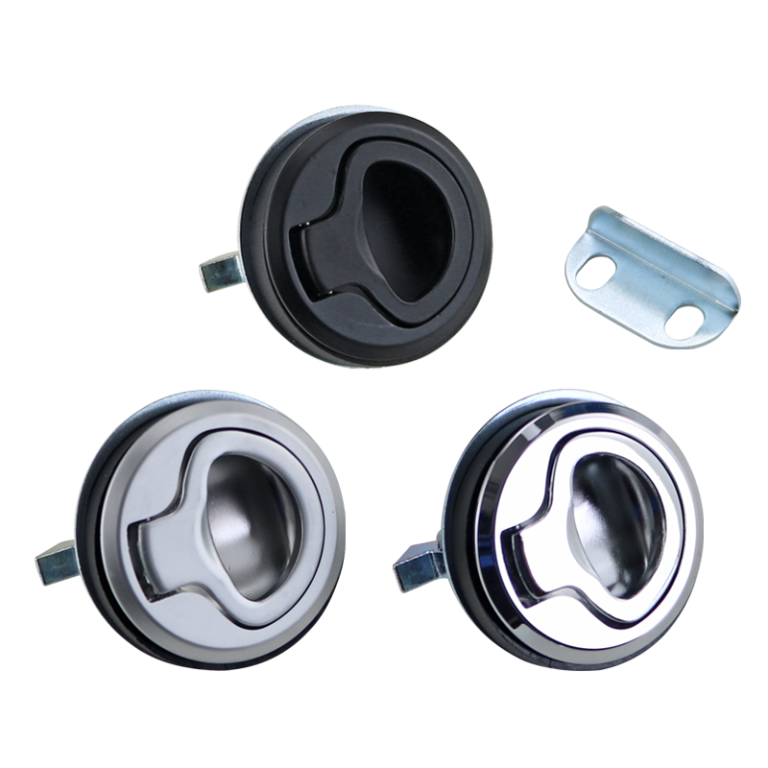
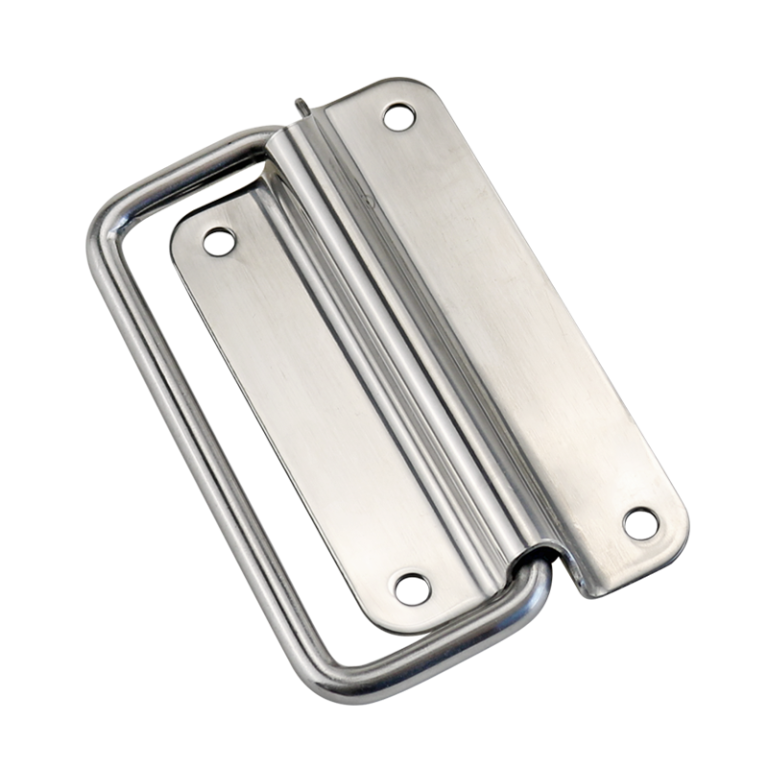
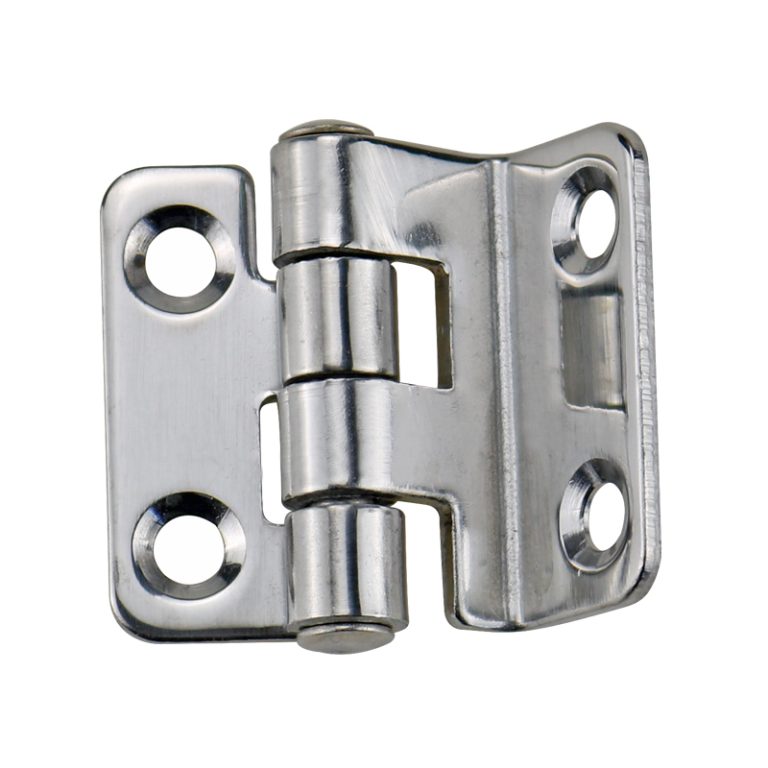
HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

Hinges are indispensable parts in daily necessities and industrial equipment.
Whether it is furniture cabinet doors, car hoods, or factory access doors, hinges bear the key functions of connection and rotation. Hinge selection is related to product performance and safety, improper selection can easily lead to door sagging, jamming or hidden danger.
This article will explain in detail the hinge material classification, common types, applicable scenes, and provide selection guide.
What Is a Hinge?
Basic Definition
Hinge is a mechanical device that consists of two metal pieces (hinge pieces) connected by a hinge pin. Its core function is to allow the object to rotate around a fixed axis, while dispersing the pressure generated by the movement. For example, a door opens and closes smoothly through a hinge, while the pivot point inside the hinge reduces friction and extends service life.
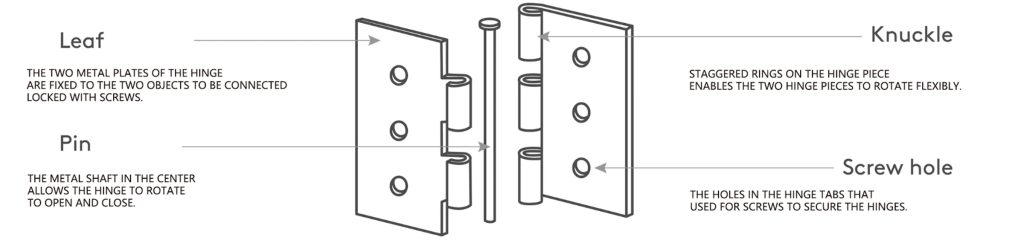
The Basic Structure of the Hinge
Hinge Piece (Leaf)
Metal piece fixed on the surface of the object, usually with mounting holes.
Hinge Section (Knuckle)
Connect the two hinge pieces of cylindrical structure, internal hinge pin.
Hinge Pin (Pin)
Inserted into the hinge section of the metal shaft, determines the hinge’s ability to rotate.
The Working Principle of the Hinge
Hinge is a mechanical device to realize rotary motion, which is composed of three parts: shaft, blade and bearing. The core principle is to provide a stable rotating pivot point through the shaft, two or more metal blades are fixed to the connecting objects (e.g. door and door frame), and the bearing structure takes the load and reduces the friction resistance. When an external force is applied to the object, the blades move in an arc around the center of the shaft, and the ball or lubricant inside the bearing makes the rotation smoother. According to mechanical design, the load-bearing capacity of hinges depends on the thickness of the shaft diameter, the thickness of the blades and the strength of the material. Common types include hinge hinges, spring hinges and concealed hinges. Modern hinges have both durability and silent effect through precision machining and surface treatment technology, which are widely used in doors, windows, furniture, industrial equipment and other fields, and are the key functional parts to realize the limited angle of the object opening and closing.
Hinge Material Classification: Metal vs Plastic
Metal Hinge
Steel Hinges
High strength, suitable for load-bearing scenarios (such as industrial doors), but need to be surface rust treatment.
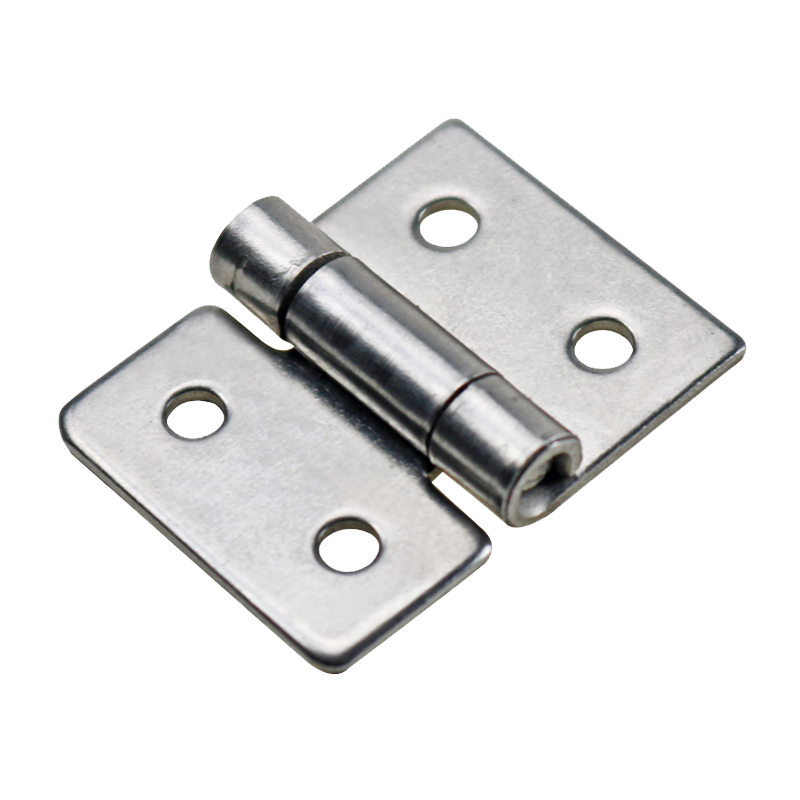

Stainless Steel Hinges
Corrosion-resistant, suitable for wet environments (such as kitchens, outdoor facilities), low maintenance costs.
Example:Stainless Steel Hinges

Brass Hinges
Decorative, suitable for furniture and retro design, but weak load-bearing capacity.
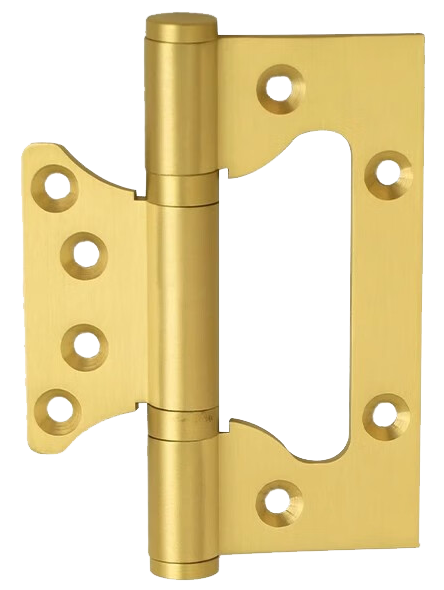
Zinc Alloy Hinges
Affordable, easy to process into complex shapes, commonly used in home appliances and light equipment.
Example:Heavy duty zinc alloy hinges
Aluminum Hinges
Light weight, good weather resistance, suitable for transportation vehicles or outdoor facilities.

Plastic Hinge
ABS Hinge
Strong impact resistance, low cost, mostly used for toys and household appliances.
Example:Black Plastic Torque Hinge
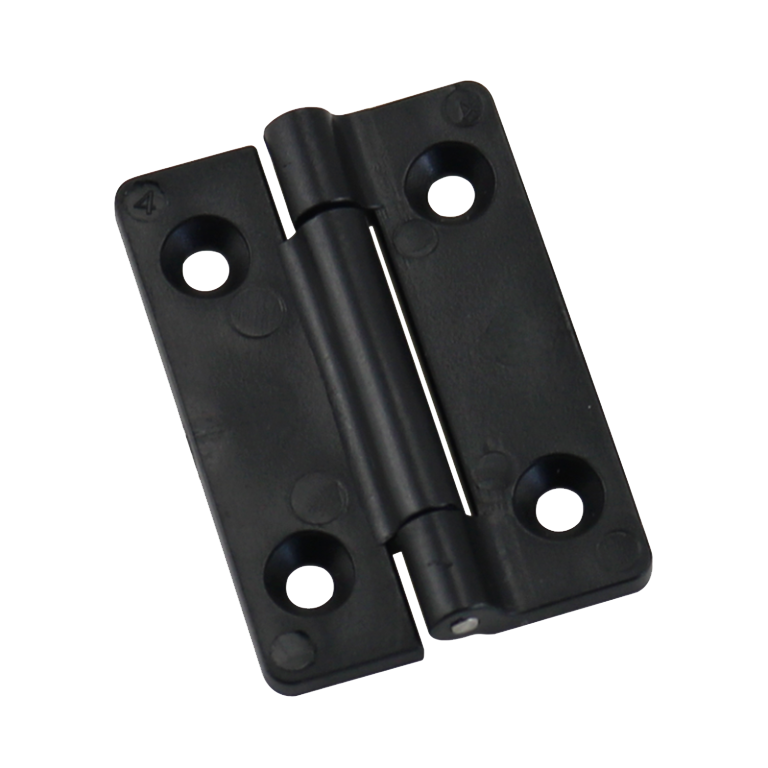

Nylon Hinges
Good flexibility, low friction coefficient, suitable for frequent opening and closing of cabinet doors.
Example:Adjustable Torque Hinge
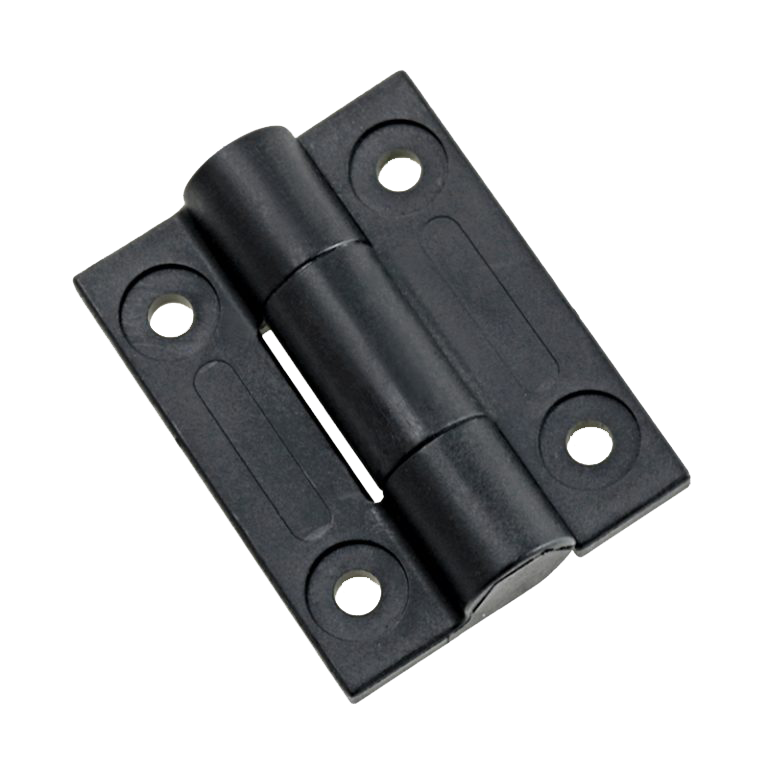

Polypropylene (PP) Hinges
Chemical corrosion resistance, anti-fatigue, commonly used in laboratory equipment.
Example:90-Degree Positioning Hinge
-768x768-1.png)
Common Hinge Types and Application Scenarios
Types of Hinges
Classified by Structure
Leaf Hinge
The most basic type, used for furniture, doors and windows.

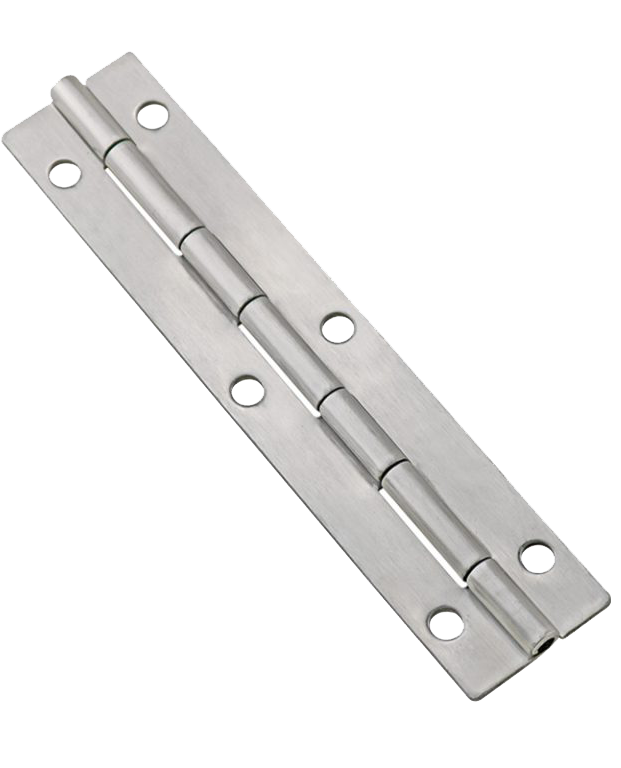
Piano Hinge
Extra long continuous design, suitable for equipment cover plate which needs even force.

Concealed Hinges
Installed inside the cabinet to maintain a neat appearance, mostly used in modern cabinets.

Functional Hinges
Automatically closes the door, commonly used in fire escape doors.

Torque Hinge
Adjustable resistance, used for laptop screens or medical instrument holders.

Specialized Hinges
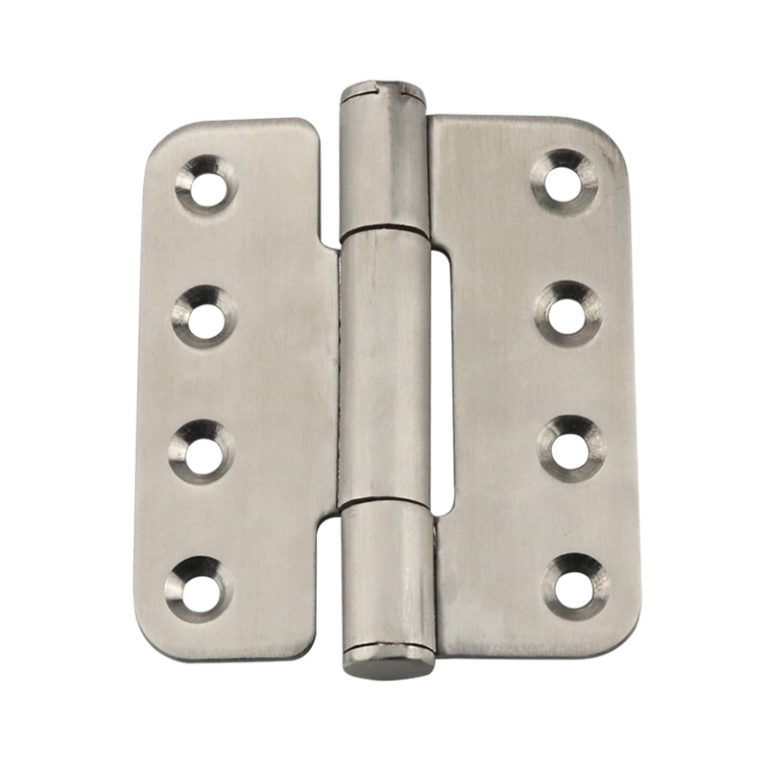
Outdoor Corrosion-Resistant Hinges
Stainless steel or galvanized to resist rain and salt spray.

Cold Storage Hinges
Used in cold storage rooms and freezers, cold-resistant.

Application Scenarios

Cabinet Doors
Keep a clean look with hidden hinges;

In Industrial Scenarios
Need to support the weight of large access panels (e.g. mechanical, electrical cabinets) to prevent deformation or falling off
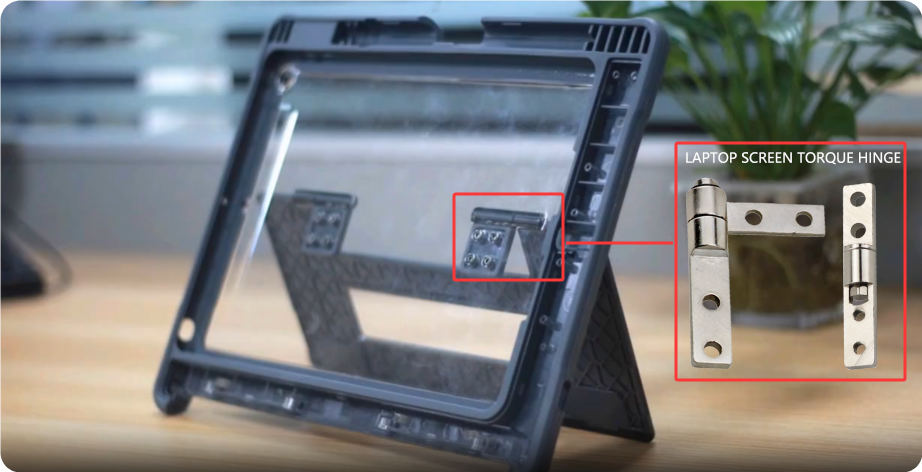
Electronic Products
Laptops, cell phones, etc. need to accurately control the screen opening and closing angle (e.g. 0-180 ° free hovering)
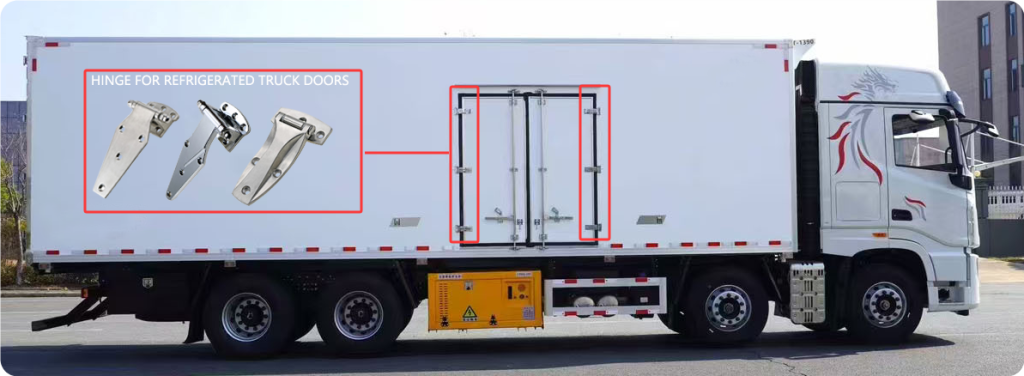
Automotive Field
Doors and hoods are exposed to rain and salt spray for a long time, so stainless steel or galvanized material is needed to prevent corrosion.
Hinge Selection Key Factors
Opening Angle
Determine the opening and closing angle of the door, different hinges support 90° to 270° rotation range.
Demand for Disassembly
Removable hinges can be separated quickly without tools, which is convenient for maintenance and repair.
Material Matching
Stainless steel for outdoor use to resist corrosion, brass/plastic for indoor decoration.
Load-Bearing
Door thickness over 40mm requires reinforced hinges to match the thickness to ensure stability.
Appearance Design
Open hinges are decorative, concealed hinges are hidden to enhance the safety and beauty.
Positioning Function
The torque hinge can realize any angle hovering/automatic return control.
Anti-Corrosion Grade
Chemical/coastal environments prioritize 316 stainless steel or Teflon coating.
Environmental Sealing
IP54 grade or above waterproof hinges are suitable for humid/dusty/extreme temperature difference environments.
Conclusion
Hinge as the core component of connection and rotation, selection needs to take into account the material, function and scene.
Metal hinges (stainless steel, steel) are suitable for load-bearing or humid environments, while plastic hinges (nylon, ABS) are suitable for lightweight or corrosion-resistant needs. Common types include concealed (cabinets), spring-loaded (self-closing) and torque hinges (screen hover).
Selection keys include load capacity, opening angle, corrosion resistance (e.g. IP54) and environmental suitability (stainless steel for outdoor use).
Industrial scenarios require reinforced hinges to prevent deformation, and electronic equipment requires precise angle control. Priority should be given to ISO certified products to ensure performance and safety.
Hinge Glossary
Basic Hinge Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Pin / Hinge | The part that connects the two leaves and provides the axis of rotation. |
| Leaf | The part of the hinge that attaches to the door and frame. |
| Pivot | The central rotating part; used in some heavy-duty hinges. |
| Opening Angle | The maximum degree to which a hinge can open (e.g., 90°, 180°). |
| Closing Force | The force exerted by the hinge when closing; some have spring-assisted closure. |
| Mounting Hole | Hole for screws to fix the hinge during installation. |
| Center Distance | The spacing between mounting holes that determines installation position. |
Construction and Mounting Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Surface Mount | The hinge is installed on the outer surface of the door and frame. |
| Concealed Mount / Hidden Mount | Hidden after installation; common in furniture applications. |
| Inset Mount | Door is fully embedded within the frame. |
| Half Overlay | Door partially overlaps the frame edge. |
| Full Overlay | Door completely overlaps the frame edge. |
| Threaded Hole | Allows screws to be driven into pre-threaded holes. |
| Weld-on Mount | Hinge is welded directly to the metal frame. |
Type Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Spring Hinge | Built-in spring for automatic closing or opening. |
| Damping Hinge / Soft-Close Hinge | Equipped with a damping mechanism to slow door closure. |
| Folding Hinge | Multi-stage foldable hinge used for folding doors. |
| Detachable Hinge | Allows for quick removal without tools. |
| Lift-off Hinge | Removable by lifting, allowing easy maintenance. |
| Heavy-Duty Hinge | Designed for high loads or large doors. |
| Continuous Hinge / Piano Hinge | Runs along the full length of the door or panel. |
| Center Hinge / Pivot Hinge | Pivot point located on or near the door’s centerline. |
Functional Features Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Self-Closing Function | Automatically closes the door after opening. |
| Stay-Open Function | Keeps the door open at a specific angle. |
| Soft-Close | Cushions the door when closing to avoid impact. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Surface treated to prevent rust or corrosion. |
| Waterproof Design | Prevents water ingress through the hinge area. |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures without deformation. |
Material and Finish Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, commonly 304 or 316 grade. |
| Carbon Steel | Strong and cost-effective, often used indoors. |
| Zinc Alloy | Aesthetic and commonly used for furniture hardware. |
| Anodized | Treated aluminum surface for enhanced corrosion resistance. |
| Galvanized | Zinc-coated surface to resist corrosion. |
| Electrophoresis | Uniform coating process to increase durability and corrosion resistance. |







