HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

In modern industry, from warehousing and logistics to data centers, cold chain facilities to offshore platforms, heavy-duty hinges play a critical role. These robust hinges must handle not just the door’s weight, but also frequent operation, heavy impacts, and harsh environments.
Studies show that using commercial-grade heavy-duty hinges can:
- Slash replacement costs by ~60%
- Reduce maintenance calls by 73% over five years
- Minimize equipment downtime and accident risks
Yet, diverse application needs demand multi-dimensional evaluation—across load capacity, corrosion resistance, lifespan metrics, and regulatory compliance (OSHA, CE, ATEX). This ensures:
- Lower lifecycle costs (-30%)
- Reduced maintenance frequency (-50%)
- Regulatory adherence
This article builds a systematic heavy-duty hinge selection methodology. Focused on technical specs, not brand endorsements, it empowers corporate decision-makers to achieve optimal hinge selection through quantitative analysis.
Read on to master a proven process—from scenario profiling to performance validation—significantly improving the science and reliability of heavy-duty hinge selection .
Defining Heavy-Duty Hinges & Key Performance Indicators
Heavy-duty hinges are engineered for loads exceeding standard doors. Their specifications far surpass household hinges.
Industry benchmarks:
- ANSI/BHMA A156.1 Grade 1: 2.5 million cycles
- ASTM B117: Salt spray corrosion testing
- Static load: >200 kg per hinge
Key Performance Dimensions
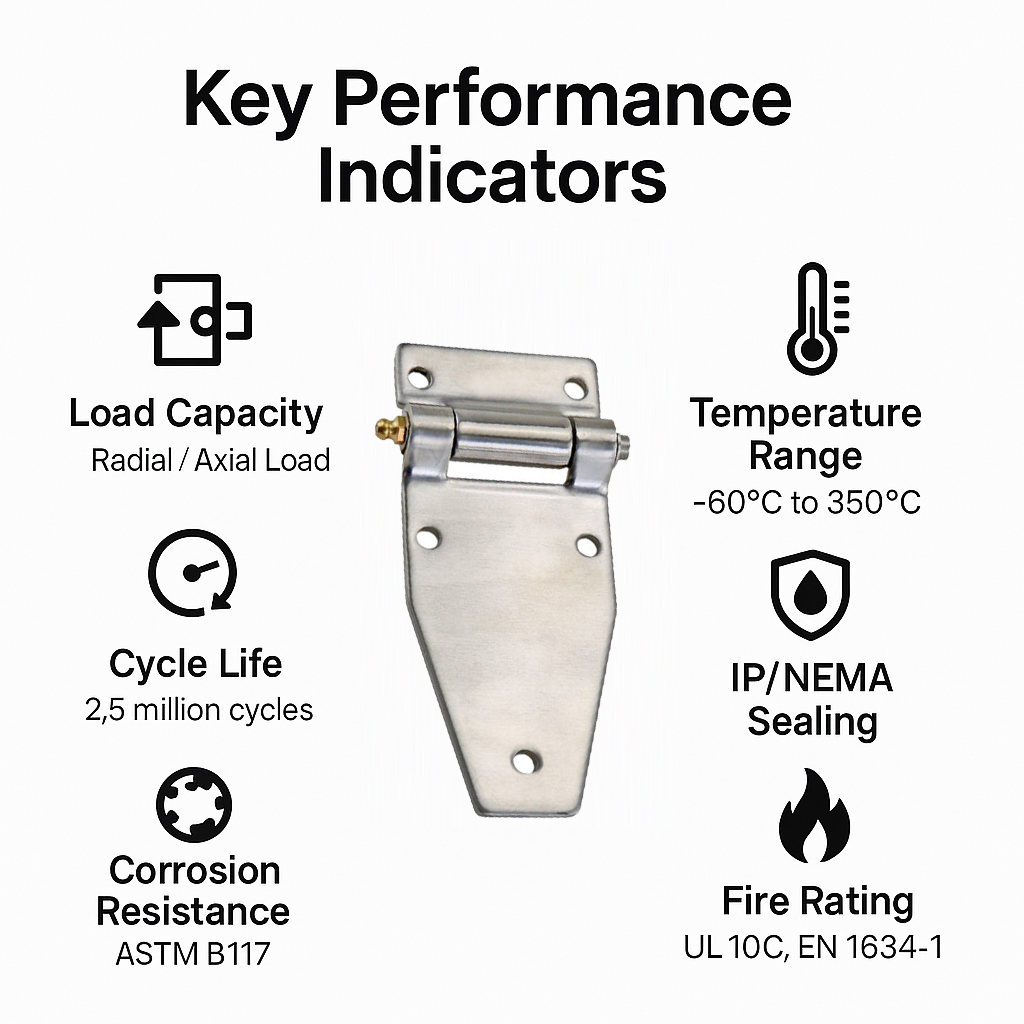
- Load Capacity: Radial, axial, and combined
- Cycle Life: Lab-tested and field-equivalent
- Corrosion Resistance: ASTM B117, ISO 9227 CASS
- Temperature Range: -60°C (-76°F) to 350°C (662°F)
- Sealing: IP/NEMA/explosion-proof ratings
- Fire Rating: UL 10C, EN 1634-1 certifications
Always verify supplier quality management (e.g., ISO 9001) and product certifications (e.g., DIN EN 1935, ANSI/BHMA A156.1).
Industrial & Commercial Application Profiles
High-Frequency Use Cases
Logistics: Loading Dock Doors
- Withstand hundreds of cycles/day & forklift impacts
- Heavy-duty hinges absorb collision energy
- Poor hinges cause door detachment, downtime, and safety issues
Pharma/Semiconductor: Cleanroom Air-Lock Doors
- Airtightness >±50 Pa pressure
- Meet GMP/ISO standards
- Stainless steel finish & continuous grounding prevent EMI and contamination
Offshore Wind Turbine Access Doors
- Face salt spray, UV, vibration
- Materials: 2205 duplex SS, special alloys
- Coatings: Weatherproof + DLC (low-friction)
- Result: 5+ years maintenance-free
Data Center Cabinet Doors
- Require EMI shielding & grounding
- Hinges provide structural and electrical support
- Ball-bearing type ensures high-cycle silent operation
Freezer/Cold Storage Doors
- Operate below -30°C (-22°F)
- Use 316L SS + PEEK bushings + cryo lubricants
- Result: Failure rate drops from 5% → 0.3% per year
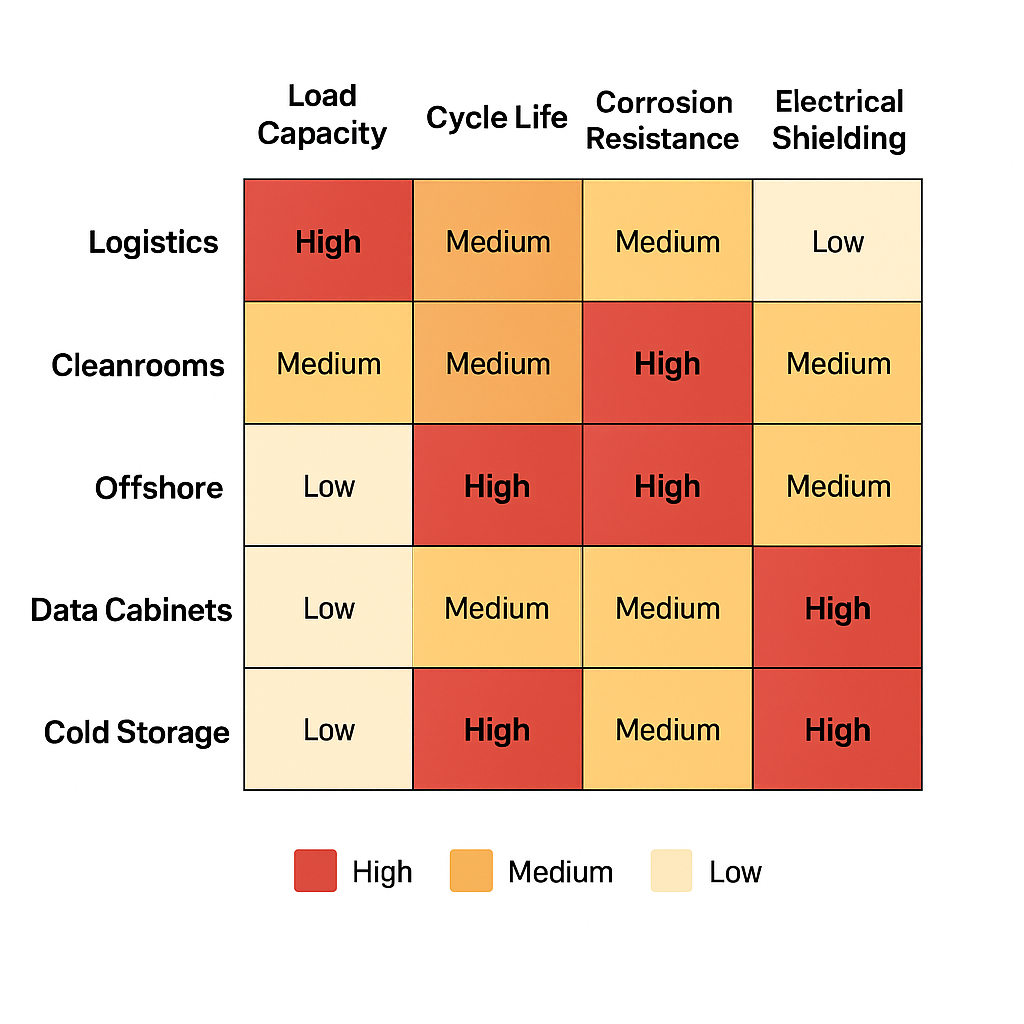
Mapping Needs to Specifications
| Industry | Hinge Priority |
|---|---|
| Logistics | Load capacity & cycle life |
| Cleanrooms | Sealing & corrosion resistance |
| Offshore | Salt spray & fatigue resistance |
| Data Cabinets | Electrical conductivity & EMI shielding |
| Cold Storage | Low-temp toughness |
Material & Manufacturing Deep Dive
Metals
- C1045 Carbon Steel: High strength + plating required
- 304 SS: Cost-effective, decent corrosion
- 316L SS: Marine-grade, added Molybdenum
- 2205 Duplex SS: 2× yield of 316L, best in chlorides
- 7075-T6 Aluminum: Aerospace-grade, 50% weight reduction, requires anodizing
Non-Metals & Composites
- PEEK Bushings: Ultra-low friction, -70°C stability
- Carbon Fiber Epoxy: 40–60% lighter than steel, ideal for trains
Manufacturing Processes
- Forging > Casting: Stronger, better fatigue strength
- 5-Axis CNC: Precision ±0.02 mm
- MIM: Cost-effective for complex shapes, cuts costs 20–25%
Surface Engineering
- Dacromet + PTFE: >2000 hrs salt spray resistance
- DLC Coating: μ=0.1–0.2, cold-temp dry-running smoothness
Hinge Types & Installation
Common Structures
| Hinge Type | Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Butt Hinges | Strongest load-bearing | Ideal for heavy industrial doors |
| Piano Hinges | Full-length support | Distributes weight evenly along the edge |
| Weld-On Hinges | No loosening, high strength | Permanent, vibration-resistant solution |
| Lift-Off/Bolt-On | Easy door removal | Tool-free maintenance and quick access |
| Adjustable Hinges | ±3 mm adjustment | Allows post-installation fine-tuning |
| Concealed vs. Exposed | Aesthetics vs. access | Hidden for clean look; exposed for ease of service |
Installation Accessories
- Reinforcement plates
- EPDM/silicone seals
- Grounding straps for EMI/ESD protection
Load Calculation & Life Prediction
Static Load
- Use 3-point load models + FEA
- Include safety margin
- Example: 100kg door → 240kg hinge load (4:1 SF)
Dynamic & Impact Loads
- Docks/wind → 5× static load
Fatigue Life
- Use S-N curves + Miner’s Rule
- Industrial: 4:1 SF, Aerospace: 8:1 SF
- Rated cycles must far exceed design life
Tools
- Excel/Python calculators
- Input: weight, hinge count, angles
- Output: Verified hinge selection
Environment & Regulatory Compliance
Harsh Environment Mitigations
- Salt Spray: Sacrificial Mg/Zn anodes
- Dust: Labyrinth seals
- High Temp: Graphite lubricants
- Low Temp: Cryo grease (-60°C)
Key US Regulations
- OSHA: ≥3mm radii, pinch-prevention
- NFPA 80: Fire door hinge count rules
- ATEX: Use non-sparking (e.g., CuBe alloy) in Zone 1+
Cost & Supply Chain Strategy
Factors Affecting Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
- Purchase Price
- Installation
- Maintenance/Repair
- Downtime
Strategies
- High-Quality Hinges → Lower TCO
- Modular Design: Standard parts reduce SKUs by 40%
- Global Sourcing:
- Germany: Precision
- China: Lead time/volume
- USA: Specialty/custom
- Specify MOQ, tolerances, RoHS/REACH
Case Studies
Cold Storage Logistics Center
- Temp: -25°C, 500 cycles/day
- Problem: Frost jamming
- Solution: 316L SS + PEEK + heaters
- Result: Failure rate → 0.3%/yr
Offshore Wind O&M Platform
- Problem: Salt, UV, vibration
- Solution: 2205 SS + DLC + weld-on
- Result: 5+ years no service, -50% maintenance dispatches
Semiconductor Cleanroom
- Specs: ISO 100, ESD, 50Pa
- Solution: Conductive hinges + seals
- Result: -30% particles, 0 ESD incidents
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Preventive Schedules
- General: Every 6 months
- Cleanroom: Every 3 months
- Offshore: Monthly
IoT Smart Hinges
- Monitor: Cycles, angles, stress
- Communication: LoRaWAN
- Benefit: Predictive maintenance
Troubleshooting (FTA)
- Common issues: Noise, sagging, corrosion
- Check: Lubrication, alignment, wear
- Solutions: Replace bushings, re-coat, weld
Rapid Field Repair
- Techniques:
- Pressurized grease
- Shim gaps
- Laser cladding (restoration)
Conclusion & Action Plan
3-Step Selection Methodology
- Profile the Scenario: Define load, environment, cycles, regulations
- Quantify Specifications: Match KPIs (load, life, corrosion, etc.)
- Validate: Lab + field testing
FAQ
When are heavy-duty hinges needed?
Use them for doors over 110 lbs, high-frequency use, extreme environments (shock/vibration/temperature), or special needs like corrosion resistance/EMI sealing.
Key specs for heavy-duty hinge selection?
Prioritize: Load capacity, lifecycle cycles, corrosion rating (ASTM B117/ISO 9227), temperature range (-60°C to 350°C), and certifications (UL/EN/ATEX).
How to calculate load capacity?
Design for 4x the door’s weight (industrial standard). Allow 5x static load for dynamic impacts. Verify with FEA analysis.
Industry-specific requirements?
Cold Chain: Sub-zero materials (-30°C)
Pharma: Sealed/sterile design
Data Centers: EMI shielding
Offshore/Wind: Salt-resistant coatings + vibration tolerance
Reducing maintenance costs?
Use forged hinges with low-friction bushings, schedule preventive maintenance, install IoT-monitored smart hinges, and choose modular designs for easy part swaps.


-1-768x768.png)




