HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

Torque-controlled hinges are precision hardware components that use internal mechanisms such as springs, friction pads, or fluid dampers to provide controlled resistance for opening and closing objects. This ensures precise positioning and smooth operation while preventing sudden movements that could cause collisions or damage. For example, they enable silent closing of bathroom doors and help protect exhibits in museum display cases. Widely used across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, they are found in home doors, windows, and cabinets, storefront entrances and office partitions, as well as industrial equipment panels. Selecting the right hinges requires careful consideration of multiple factors, while proper installation and adjustment are crucial for optimal performance. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and inspections, helps ensure long-term stability and reliability.
I. Introduction to Torque-Controlled Hinges
1. Definition and Basics
Torque-controlled hinges are specialized hinges designed to provide controlled resistance when opening and closing. This resistance, known as torque, ensures smooth operation and precise positioning. For example, in a laptop screen hinge, torque control prevents the screen from falling shut or flopping open abruptly.
2. Working Principle
Torque hinges achieve control through internal friction mechanisms, such as springs, friction pads, or fluid dampers. The magnitude of torque determines how much resistance is applied. For instance, a cabinet door with a torque hinge will stay open at a desired angle rather than swinging freely.
3. Market Significance
The growing demand for torque-controlled hinges stems from their increasing application in high-end furniture, medical devices, and automotive systems. They provide enhanced user experience by improving safety and convenience, making them a crucial component in modern hardware solutions.
II. Unmatched Flexibility and Customization
1. Customization Options
Manufacturers offer adjustable torque settings to suit various applications. For instance, a torque hinge used in a car’s glove compartment might require lower torque than one in an industrial control panel door.
2. Design Adaptability
Torque hinges can be customized to fit different architectural styles. For example, luxury hotel doors may require concealed torque hinges for a sleek, modern appearance, while industrial setups may prioritize heavy-duty, externally mounted hinges.
3. User-Centric Flexibility
Users can easily adjust or select torque levels based on their specific needs. For example, a hospital bed’s adjustable screen hinge can be tailored for easy repositioning by medical staff without requiring extra force.
III. Applications of Adjustable Torque Hinges
1. Residential Uses
Homeowners benefit from torque hinges in applications such as front gates that remain open at a set angle, or kitchen cabinets that close gently without slamming.

2. Commercial Uses
In retail, storefront doors with torque hinges allow controlled movement to prevent sudden slamming, which enhances customer safety. Office partition doors also use them for effortless and controlled operation.

3. Industrial Uses
Industrial settings require torque hinges for access panels on machines, where controlled opening and closing prevent sudden movements that could damage equipment or cause injuries.
IV. Advantages of Torque-Controlled Hinges
1. Smooth Operation
A torque hinge in a self-closing bathroom stall door ensures silent and controlled closing, reducing noise and increasing privacy.
2. Damage Prevention
By minimizing abrupt movements, torque hinges extend the lifespan of doors and panels. For example, in a museum display case, they prevent glass panels from slamming shut and cracking.
3. Precision Control
Torque hinges in aerospace applications, such as cockpit control panels, ensure precise positioning and secure operation even under extreme conditions.
V. Selecting the Right Torque Hinge
1. Dimensional Considerations
A large industrial access panel requires a hinge with higher torque capacity than a small residential cabinet door.
2. Weight-Based Selection
Heavy-duty torque hinges are needed for armored vehicle doors, whereas lighter versions suffice for an office workstation’s foldable monitor stand.
3. Managing Torque Intensity
For baby-proofing applications, torque hinges ensure that cabinet doors resist easy opening while still being accessible to adults.
VI. Special Considerations
1. Environmental Factors
Outdoor applications require corrosion-resistant torque hinges, such as those found in marine vessels where exposure to saltwater could degrade standard hinges.
2. Frequency of Use
A high-traffic airport restroom door will need a durable torque hinge capable of enduring thousands of operations per day, while a rarely used attic door requires a lower-duty solution.
3. Aesthetic Preferences
High-end furniture designers may prefer hidden torque hinges for a seamless look, while industrial environments prioritize durability over aesthetics.

VII. Installing Torque Hinges
1. Tools Required
Common tools include screwdrivers, wrenches, and alignment gauges to ensure precise installation.
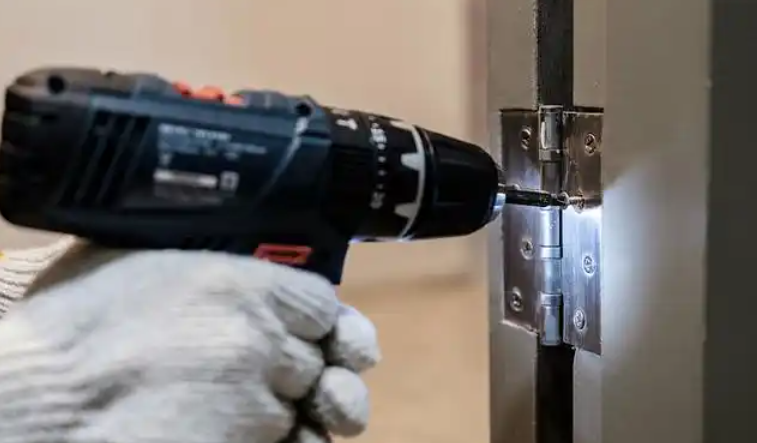
2. Step-by-Step Installation Guide
正确的安装包括标记铰链位置、钻引导孔以及用适当的紧固件固定铰链以防止错位。
3. Pre-Installation Checks
Verifying weight capacity and torque rating before installation prevents future operational issues.
VIII. Adjusting Torque Hinges
1. Torque Adjustment Process
笔记本电脑屏幕上的扭矩铰链可能需要进行微调,以保持所需的开启阻力,而不会使屏幕太硬。
2. Fine-Tuning for Optimal Performance
Ensuring the correct torque balance in a self-closing gate prevents it from slamming shut or staying open unintentionally.
3. Common Adjustment Mistakes
Over-tightening a torque hinge in a cabinet can make it too difficult to open, while under-tightening may result in unintended movement.
IX. Importance of Precision in Installation and Adjustment
1. Performance Impact
Misaligned torque hinges in a vehicle’s trunk lid can lead to uneven weight distribution and premature failure.
2. Safety Considerations
A poorly adjusted torque hinge on a medical equipment access panel can pose risks if it fails to hold its position during use.
3. Long-Term Durability
Properly installed torque hinges in military applications ensure longevity and reliable performance in extreme environments.

X. Precautions During Installation and Adjustment
1. Handling Hinge Components
Improper handling of precision-engineered hinges can lead to performance degradation over time.
2. Using Tools Safely
Always use recommended tools to prevent damaging the hinge mechanism during installation.
3. Following Manufacturer Guidelines
Deviation from guidelines can result in compromised hinge performance and voided warranties.
XI. Common Installation Issues
1. Alignment Problems
An unaligned torque hinge on a glass door can lead to uneven stress distribution, increasing breakage risk.
2. Torque-Related Issues
A torque hinge with too much resistance in a robotic arm could reduce efficiency and increase energy consumption.
3. Mounting Challenges
Improperly secured torque hinges may cause panel doors in industrial equipment to rattle or detach over time.
XII. Solutions for Installation Issues
1. Fixing Alignment Problems
Using a leveling tool and repositioning the hinge can correct misalignment issues.
2. Correcting Torque Issues
Fine-tuning the hinge using the adjustment mechanism ensures the correct balance of force.
3. Improving Mounting Security
Utilizing stronger fasteners and ensuring proper torque settings can prevent loosening over time.
XIII. Maintaining Torque Hinges
1. Regular Cleaning
Removing dust and debris prevents premature wear, especially in industrial environments.
2. Lubrication
Applying the correct lubricant at recommended intervals ensures smooth operation and extends hinge lifespan.
3. Periodic Inspection
Checking for wear signs ensures early detection of issues before complete failure occurs.
XIV. Troubleshooting Torque Hinges
1. Unusual Noises
Applying lubricant or adjusting fasteners can resolve squeaking or grinding sounds.
2. Difficulty in Operation
Adjusting torque settings or realigning the hinge can restore optimal movement.
3. Hinge Failure
Replacing worn-out hinges with suitable alternatives prevents further operational issues.
This guide provides a thorough understanding of torque hinges, their selection, installation, adjustment, and maintenance. Their versatility across industries ensures that they remain a vital component in modern hardware solutions.







