HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

What Is a Swivel Torque Hinge?
swivel torque hinges include a torque mechanism that allows them to stop at any position (arbitrary stop).
These hinges are commonly used in the movable parts of devices such as tablet stands and machine tool control panels. Another feature of swivel torque hinges is that the center hole can be used to pass wires through. If you need to pass wires through, please select a swivel torque hinge with a suitable hole diameter.
The Core Difference Between a Swivel Torque Hinge and a Standard Hinge
- Ordinary hinges: Door panels can swing freely without resistance. Doors can either be fully open or fully closed and cannot be stopped at intermediate positions.
- Swivel torque hinges: Provide continuous rotational damping force. Door panels can remain stable at any position within the 0° to 180° (or larger angle) range.
Principle of Rotational Damping
Friction Principle (Most Common)
- Utilizes controlled friction force generated between precision-designed friction plates and metal shafts or housings.
- During rotation, friction force resists movement, generating torque. Adjusting the pressure or material of the friction plates can alter the torque magnitude.
Spring Principle
- Utilizes the preload force of disc springs or torsion springs.
- During rotation, the spring is compressed or twisted, generating a counteracting rebound force as damping.
- Commonly used in scenarios requiring large torque or specific angle positioning.
Torque hinge function demonstration
Core Structure and Operating Mechanism
Key Components
- Shaft: Core rotating component, fixed to one side (e.g., door panel).
- Housing: Fixed to the other side (e.g., equipment body); contains the torque mechanism.
- Torque-generating mechanism:
- Friction-type: Friction plates, pressure adjustment devices.
- Spring-type: Coil/torsion springs, cams, positioning balls/grooves.
- Mounting Plate/Bracket: For securing the hinge to body and moving parts.
Differentiation of Torque Hinges
Unidirectional vs. Bidirectional Torque
Unidirectional: Resistance in opening direction only; used for lids that need to stay open.
Example: One-way torque hinge

Bidirectional: Resistance in both directions; allows the part to stop at any position. Most common type.
Example: 360-degree swivel torque hinge

Fixed Torque vs. Adjustable Torque
Fixed: Pre-set torque value. Cost-effective. For clear, consistent requirements.
Example: 360-degree swivel torque hinge

Adjustable: User-adjustable torque for design flexibility and field tuning.
Example: 360-degree adjustable torque hinge

Common Applications of Swivel Torque Hinges
Fixed Swivel Torque Hinge
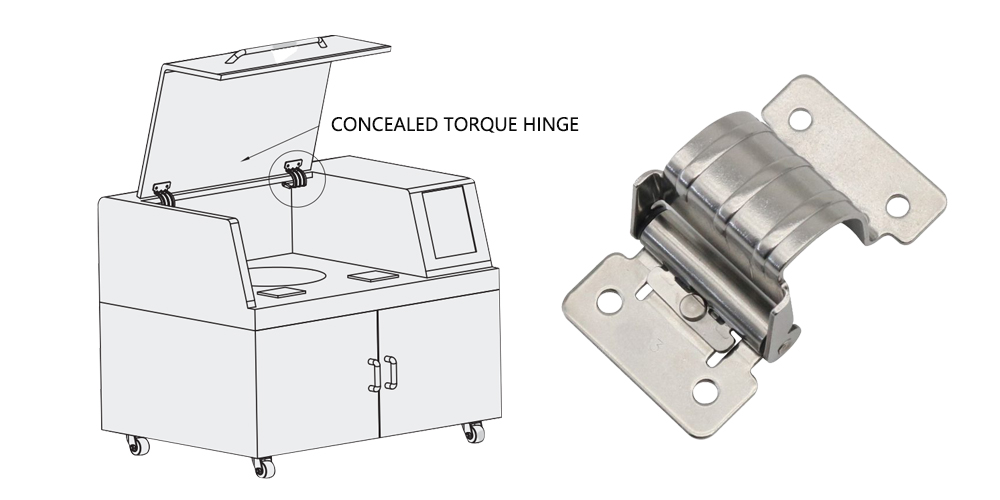
- Features: Constant torque value, non-adjustable, simple structure.
- Applications: Small maintenance covers, lightweight lids, cost-sensitive environments.
Free-Stop Swivel Torque Hinge
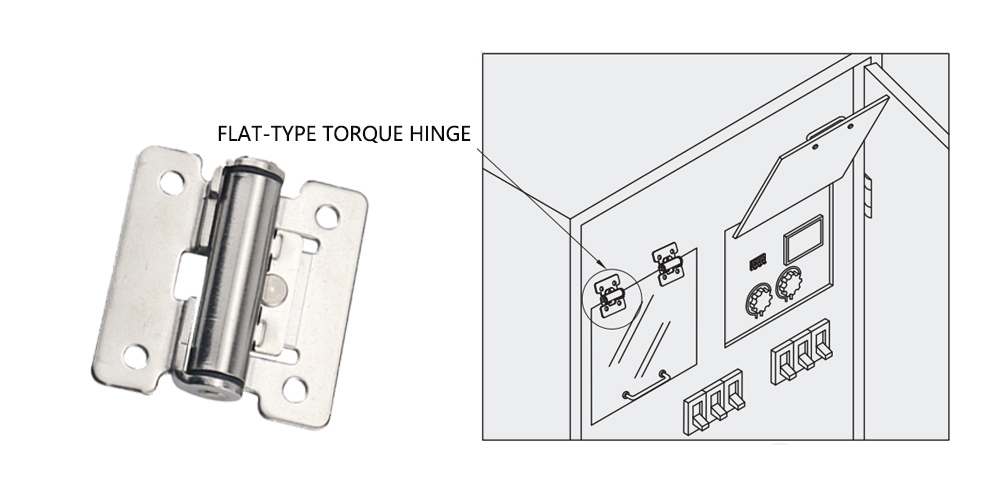
- Features: Continuous damping torque. Can stop at any angle.
- Applications: Display/control panels, equipment doors that stay open.
Dual axis torque hinge
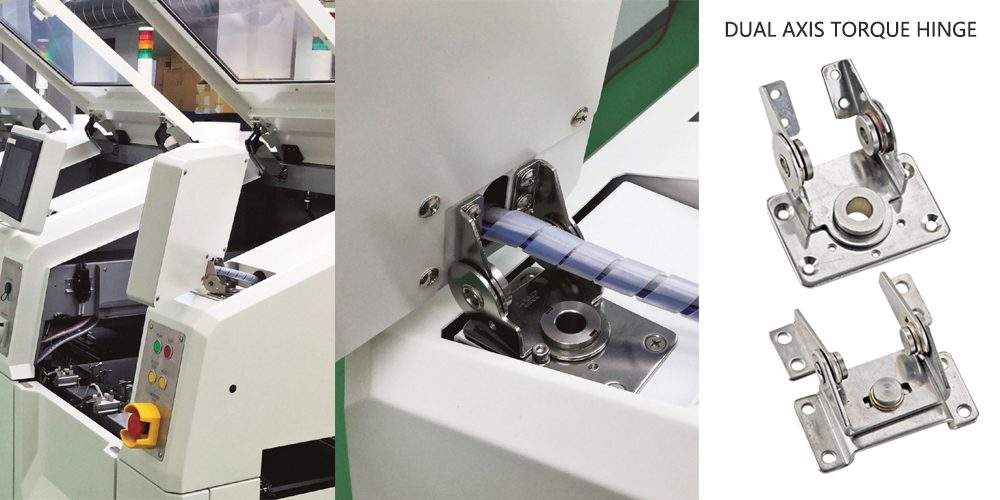

- Features: Two distinct torque levels at different rotation stages.
- Applications: Server doors, applications needing tactile feedback.
Positioning Rotary Torque Hinge
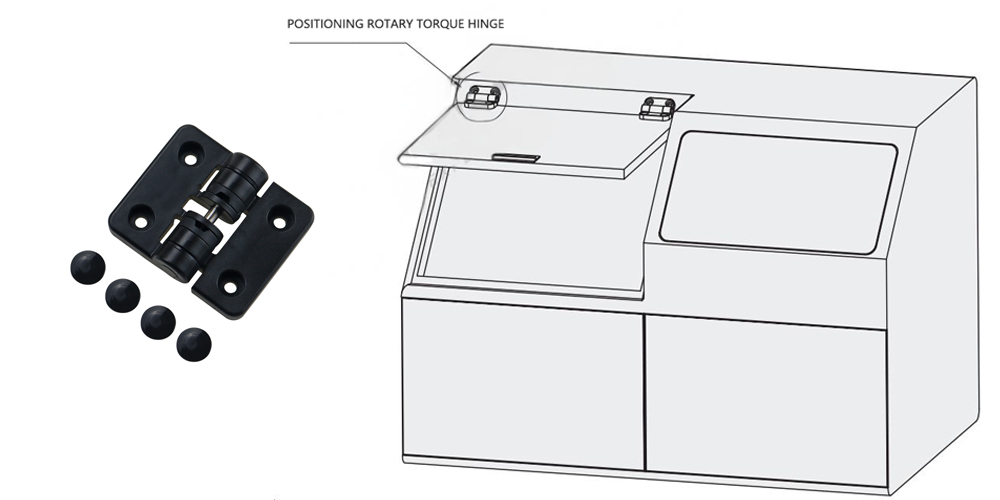
- Features: Can stop at preset angles (such as 0°, 45°, 90°, 105°) and has a damping function.
- Suitable for car glove compartments, dashboards, folding tables, and lamps.
Material Selection for Torque Hinges
Stainless Steel
- Extremely high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good temperature resistance.
- Most commonly used and reliable, especially suitable for rotating torque hinges.
- Used in medical sterilization, food, outdoor, and marine equipment.
- And high humidity and corrosive environments such as chemical plants and laboratories.
Aluminum Alloy
- Lightweight and lower cost than stainless steel.
- Has a certain degree of corrosion resistance after anodizing.
- Strength and wear resistance are generally not as good as stainless steel.
- Used in applications requiring weight reduction, general industry, and consumer electronics.
- Load capacity and environmental corrosion resistance must be assessed.
Engineering Plastics
- Extremely lightweight, low cost, insulating, and non-magnetic.
- Some have good chemical resistance.
- Strength, stiffness, and temperature resistance are far inferior to metals.
- May age and creep, affecting torque stability.
- Used in light-load applications, small electronic covers, and applications requiring insulation.
Key Durability Metrics
- Corrosion resistance: Stainless steel hinges (e.g., 316 grade) are preferred for outdoor, medical, marine, and chemical applications.
- Chemical corrosion resistance: Confirm material compatibility when exposed to chemical agents.
- Wear resistance and lifespan: The wear resistance of friction components determines hinge lifespan.
How to Select the Appropriate Swivel Torque Hinge
Torque Requirements
- Calculate weight × lever arm (distance from hinge axis).
- Include safety factor of 1.2–1.5 and external accessories in design.
Motion and Installation Characteristics
- Define angle range, damping speed, and mounting method.
- Ensure correct dimensions and axis alignment.
Durability and Environmental Conditions
- Estimate opening frequency (e.g., 10,000 or 100,000 cycles).
- Choose materials based on exposure conditions and IP rating needs.
Special Features
- Torque adjustment, locking, free-stop, aesthetic needs, etc.
Demonstration of positioning hinge installation
Installation and Maintenance Recommendations
Installation Notes
- Use correct screws and torque per manual.
- Ensure shaft alignment across hinges to avoid:
- Stress concentration
- Abnormal noise
- Torque loss or premature failure
- Install on flat, rigid surfaces. Avoid overloading with large doors.
Maintenance Recommendations
- Maintenance-free design: Do not open or oil the hinge.
- Avoid lubricants: Using regular oils can destroy friction-based torque.
- Cleaning: Use mild cleaner. Avoid pressure washing or chemical exposure.
- Adjustable hinge tuning: Use proper tools, adjust gradually, avoid over-tightening.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Precise angle holding
- Space-saving design
- Mechanical simplification
- Enhanced perceived value
- Improved safety
Limitations
- Higher cost
- Limited torque/angle range in some designs
- Unsuitable for extremely heavy or shock-loaded applications
- Not for high-frequency use
- Strict installation requirements
Summary
Swivel torque hinges are indispensable components in modern industrial design, offering precise, stable positioning without additional support structures. To apply them successfully, designers must understand torque mechanisms, types, materials, environment suitability, and installation criteria—especially axis alignment and load calculation.
FQA
Q: Are torque hinges the same as friction hinges?
A: Yes, they are the same. Friction hinges are a type of torque hinge.
Q: Can swivel torque hinges be used outdoors?
A: Stainless steel must be used for outdoor use.
Q: How do you select the torque value for a swivel torque hinge?
A: You need to calculate the weight × center of gravity distance.
Q: Can swivel torque hinges stop at any position?
A: Arbitrary stop types are possible, but limit types are not.


-768x768.png)