HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.
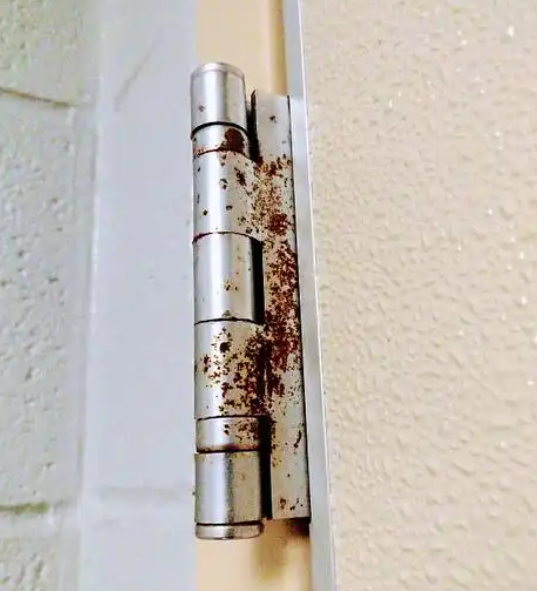

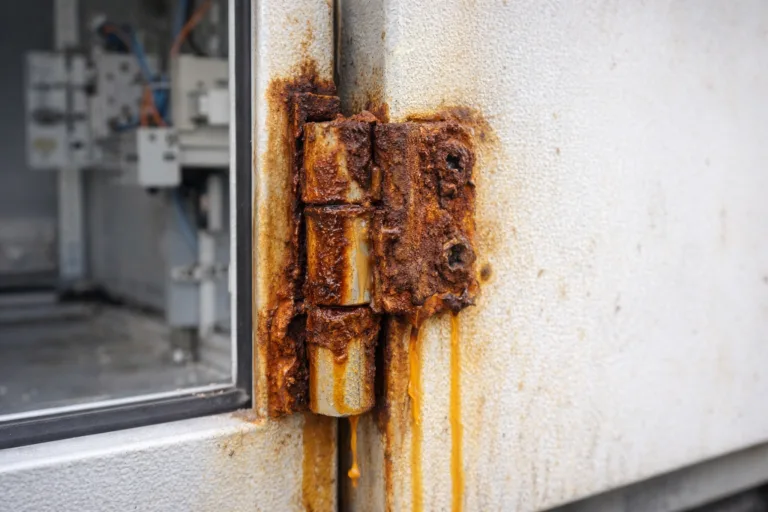
In the chemical industry, marine engineering, sewage treatment and other industrial fields, equipment in the long-term high humidity, salt spray erosion and acidic and alkaline media environment, frequent opening and closing of the door/cabinet metal hinges are prone to corrosion, jamming or even deformation and fracture.
This corrosive failure not only destroys the equipment airtightness and structural stability, but also may lead to mechanical failure, material leakage and other structural risks due to the fall of the door, significantly increasing the pressure of production safety control and equipment maintenance costs.
Why must industrial environments use corrosion-resistant hinges?
Common types of corrosive environments
- Marine environment: high salt spray, high humidity accelerate metal oxidation
- Chemical workshop: acid and alkali vapor, solvent liquid direct contact
- Food processing plant: high temperature water vapor and detergent repeated erosion
- Outdoor power cabinets: rainwater infiltration and condensation due to temperature difference
The harm of corrosion on hinges
- Functional failure: rust leads to hinge rotation jamming, the door can not be opened and closed properly.
- Structural weakening: metal corrosion leading to load-bearing failure and increased risk of door dislodgement.
- Safety Hazard: Rust debris dispersal jeopardizes line cleanliness/degradation of equipment insulation.
Corrosion resistance comparison of 5 common hinge materials
| Material | Corrosion resistance | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless steel 316 | ★★★★★ | Strong corrosion resistance to chlorine ions | Price 40%-50% higher than 304 | Desalination equipment, chemical plants |
| Stainless steel 304 | ★★★★☆ | Cost-effective, versatile | Easy to rust in long-term salt spray environment | General industrial plant |
| Aluminum alloy | ★★★☆☆ | Light weight, easy to process molding | Low strength, not acid and alkali resistant | Electronic equipment shells |
| Engineering plastics | ★★★★☆☆ | Completely rust-proof, good insulation | Easy to aging, not resistant to high temperature | Medical instruments, food processing equipment |
| Galvanized steel | ★☆☆☆☆ | Lowest cost | Rapid rusting after coating breakage | Dry indoor environment |
the typical industrial scenarios of hinge selection program
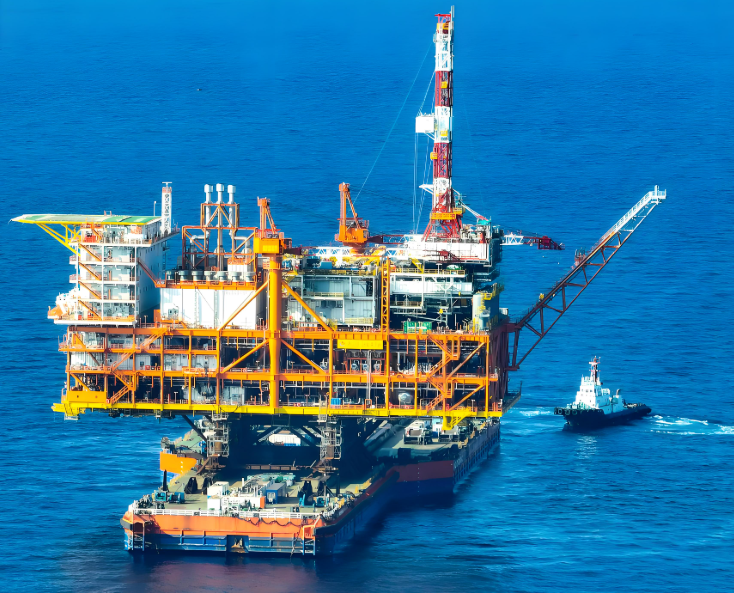

Coastal equipment and offshore platforms
- Recommended material: 316 stainless steel with self-lubricating bearings for heavy-duty hinges
- Key indicators: IP66 waterproof rating, screw holes need to be sealed.
- Tips: Avoid using hinges with copper parts.

Chemical acid and alkali environment
- Recommended solution: PP plastic + 316 stainless steel mandrel combination hinge
- Design Points: Adopt full covering structure to prevent liquid from seeping into the rotating part.

Food and Pharmaceutical Workshop
- Compliance requirements: 316L stainless steel certified by FDA or EC1935.
- Designed for cleaning: Seamless surfaces, supports high pressure water jet flushing.
- Alternative: PEEK engineering plastic hinge
3 key factors to improve the corrosion resistance of hinges

Surface treatment process comparison
| Process | Cost | Salt spray resistance | Applicable materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrophoretic coating | Medium | 800 hours | Steel, aluminum alloy |
| Dacromet coating | High | 1200 hours | High strength steel |
| Anodizing | Low | 400 hours | Aluminum alloy |
| PTFE coating | Very high | 2000 hours | Stainless steel, titanium alloy |
Structural design details
- Drainage holes: 0.5-1mm drainage holes at the bottom of the hinge (e.g. German Hettich outdoor hinge design)
- Concealed pivot: prevents corrosive media from accumulating in the pivot area.
- One-piece molding: reduces welding or splicing gaps.
Influence of installation method
- Mistake: Exposed screws lead to waterlogging and rusting.
- Correct practice: use stainless steel socket head cap screws + silicone sealing gasket
corrosion-resistant hinge selection checklist
Environmental analysis
- Daily temperature and humidity change range?
- Types of corrosive media contacted (acidic/alkaline/salt spray)?
Mechanical requirements
- Door body weight (light <20kg choose aluminum alloy, heavy >50kg with stainless steel)
- Number of openings per day (high frequency with self-lubricating structure)
Compliance Certification
- Is RoHS/REACH environmental certification required?
- Special industry standards
Cost Tradeoffs
- Does the budget allow for 316 stainless steel?
- Consider full life cycle costs (low cost hinges may increase maintenance costs)
Supplier Evaluation
- Request material testing reports
- Confirmation of surface treatment process details (plating thickness ≥ 20μm)
FAQ
Q1: The most corrosion-resistant hinge material?
A: Hastelloy/titanium alloy for extreme environments, and 316 stainless steel for regular selection.
Q2: How to extend the life of industrial hinges?
A: Regular lubrication, avoid overloading, choose 316 stainless steel material.
Q3:What are the main indicators for hinge selection?
A: Corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, environmental suitability and cost.
Conclusion
In a highly corrosive environment, the selection of corrosion-resistant hinges directly determines the safety of the equipment, which requires comprehensive consideration of the material (preferably 316 stainless steel/engineering plastics), the surface treatment process, the structure of the sealing and the installation of adaptability, in order to match the extreme conditions to achieve long-lasting stable operation.