HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

Modern industrial environments push cabinet door hinges to their limits. Think daily operations with hundreds of door cycles. Exposure to corrosive chemicals, abrasive dust, and constant vibration. Control cabinets needing frequent access. Heavy machinery doors bearing significant weight under vibration. Outdoor cabinets facing salt spray and extreme weather.
Traditional hinges often fail here. Bolts loosen. Steel pins seize with rust. Maintenance becomes a nightmare, requiring full door or cabinet removal. Misalignment and noise plague long-term operation.
The Pain Points of Traditional Hinges
Cumbersome Maintenance
Replacing or servicing standard hinges means removing the entire door or cabinet. This wastes time and effort.
Seized Pins
Carbon steel pins in standard hinges rust and seize quickly in damp conditions. Removing them becomes extremely difficult.
High Replacement Costs
Damaged components force full hinge replacement. This spikes spare parts costs and costly downtime.
Limited Flexibility
Traditional designs lack quick-release features. Installation and adjustment are difficult. They struggle with micro-adjustments or varied opening angles.
Why Removable Pin Weld-On Hinges Excel
Welded Stability
These hinges fuse permanently to the cabinet via welding. This creates an incredibly strong, vibration-proof connection. It eliminates bolt loosening. Precise alignment minimizes door sag. Door operation stays smooth.
Quick-Release Flexibility
The removable pin design incorporates quick-release functionality. Spring clips or set screws allow tool-free pin removal. Technicians simply pull the pin to detach the door. Maintenance speed increases dramatically.
Strength Meets Serviceability
Removable pin weld-on hinges merge permanent welded strength with easy repairability. They handle heavy loads and simplify maintenance. This is a revolutionary upgrade over traditional hinge technology.
Technical Principles & Core Design
Breaking Down the Structure
Weld-On Leaf
Made from strong cold-rolled steel or stainless steel. This leaf welds directly to the door or cabinet frame. It delivers exceptional structural strength. For example, SPEP highlights cold-rolled steel weld-on hinges offer great cost-effectiveness and durability under heavy loads. Welding eliminates drilling, bolts, loosening, and misalignment.
Removable Pin
Features quick-release mechanisms like set screws or spring clips. WDS Components notes their removable pin hinges use spring-release systems. This allows tool-free pin removal. Pins often have detent grooves or clip positions. Secondary safety features, like retaining rings, prevent accidental pin dislodgement during door operation.
Bearing/Bushing System
Heavy-duty weld-on hinges often use brass bushings or ball bearings at the pin-leaf interface. This reduces friction, distributes load, and ensures smooth operation. It extends hinge life and load capacity. High-temp or corrosive environments benefit from solid lubricants or specialized greases.
Engineering Advantages of Welded Installation
Permanent Fixing
Welding bonds the hinge and cabinet into a rigid unit. Unlike bolted hinges, vibration cannot cause loosening or shifting. As HardwareSource states, weld-on hinges handle significant weight and long-term use via surface welding. Bolted hinges loosen over time, needing constant retightening.
Uniform Stress Distribution
Welding spreads stress across the entire weld area. Loads distribute evenly over large weld points. This boosts structural integrity for heavy doors. Machine Design emphasizes that precise weld-on hinge installation reduces door sag. It’s ideal for doors needing tight fitment.
High Load Capacity
Weld-on hinges use robust, rigid materials designed for heavy loads. SPEP states their cold-rolled steel weld-on hinges excel in high-weight applications. This high capacity supports large cabinet doors or industrial hatches reliably. Fewer hinges are often needed.
The Innovation of the Removable Pin
Tool-Free Removal
Innovative mechanisms let technicians eject pins quickly. Use a punch, pull hook, or button. No tools are required for door removal. WDS Components confirms their quick-release hinges enable “tool-free door panel removal and reinstallation.” This drastically cuts repair time.
Safety Locking
Safety locks or detents on the pin head prevent accidental release. Even under vibration or heavy loads, the pin stays secure. Some designs add spring returns or dual retaining clips for extra security.
Corrosion-Resistant Materials
Pins and leaves use high-strength carbon steel or stainless steel. Heat treatments like carburizing increase hardness. For harsh chemical or coastal settings, choose 316L stainless steel or zinc/nickel plating. Research shows 316L withstands 1000+ hours of salt spray testing with minimal corrosion. Perfect for extreme environments.
Load Capacity & Mechanical Performance
Cycle Life Testing
Removable pin weld-on hinges undergo rigorous fatigue testing. ANSI/BHMA A156.1 requires Grade 1 Heavy-Duty hinges to survive 2.5 million open/close cycles. After millions of operations, the hinge must remain intact and tight.
Corrosion Resistance
ANSI/BHMA standards mandate salt spray testing (ASTM B117). Testing proves 316L stainless steel vastly outperforms standard steel. For instance, untreated 316L samples show almost no corrosion after 4000 hours of salt spray. This makes it ideal for high-corrosion hinge parts.
Applications & Core Advantages
Key Industrial Applications
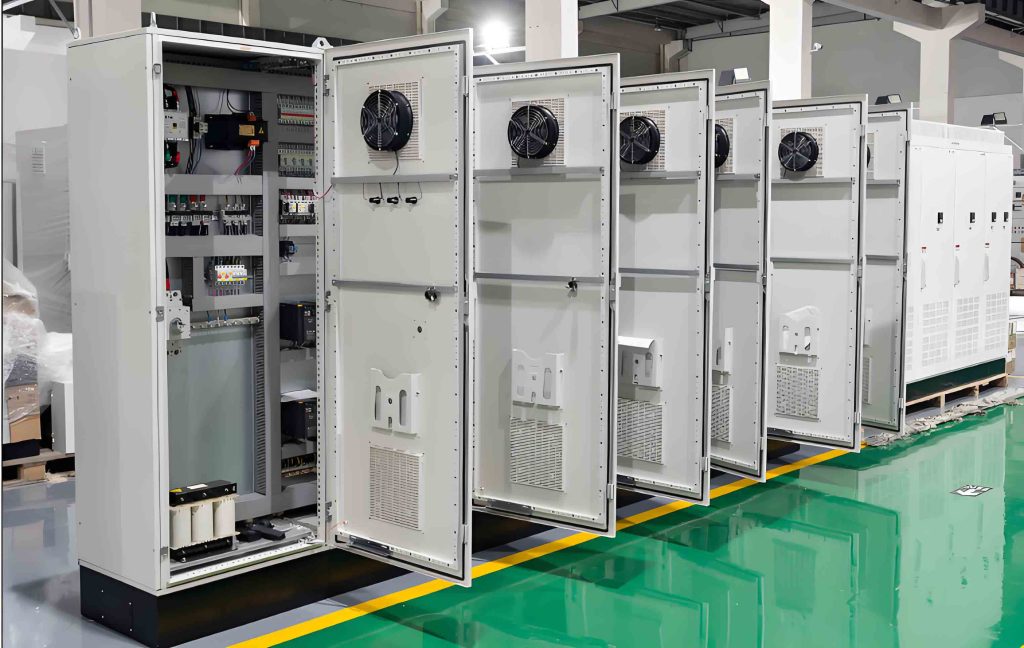

Application of Removable Pin Weld-On Hinges in Electrical Control Cabinets
Electrical Control Cabinets
House sensitive electronics needing frequent access. Removable pin weld-on hinges let technicians detach a single door. No need to remove the entire cabinet or internal components. Maintenance efficiency soars.
Machine Guard Doors
Endure intense vibration and dynamic loads. The robust design of weld-on hinges carries door weight steadily. Welded mounting minimizes vibration-induced fatigue. It also strengthens the overall structure.
Chemical & Explosion-Proof Cabinets
Face strong corrosive agents. Hinge materials need superior corrosion resistance. Opt for 316L stainless steel with plating. Weld-on hinges also improve door sealing. Their gapless design supports explosion-proof safety requirements.
Outdoor Enclosures
Battle extreme temperatures, rain, and wind. Cabinet door hinges must meet high IP ratings like IP66. IP66 demands total dust protection and resistance to powerful water jets. Weld-on hinges using stainless steel and seals ensure high protection. They keep out particles and moisture.
(Image: Industrial control cabinet door side view. Shows weld-on removable pin hinge. Pin removal allows independent door detachment for easy maintenance.)
Deep Dive: Core Advantages
Superior Maintenance Efficiency
Traditional repairs require full door removal. Removable pin hinges allow single-door detachment. Technicians avoid removing other doors or internal parts. Maintenance time plummets. Compared to old hinges, replacement time drops from hours to minutes. Downtime costs shrink significantly.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Modular damage control! Replace only the damaged pin or leaf. No need for full hinge replacement. This cuts spare parts inventory and procurement costs. One automotive line saved thousands annually on downtime using these hinges.
Installation & Adjustment Flexibility
Assemble leaves and roughly position before welding. Fine-tune alignment after welding using adjusters. Even post-installation, removing the pin allows slight door shifting. Achieve perfect, uniform door gaps (recommended 2-3 mm). Some removable pin hinges offer multi-angle mounting (-30° to 120°). They adapt to unique space needs.
Extreme Environment Durability
Meet IP66 demands with sealed hinge designs. Combine corrosion-resistant materials and coatings. These weld-on hinges thrive outdoors or in harsh settings like food processing. 316L stainless steel offers exceptional salt spray resistance. Add zinc plating or epoxy coating. Endure 2000+ hours of salt spray testing. Guarantee long-lasting performance.
Professional Installation & Welding Guide
Pre-Installation Prep
Clean hinge mounting areas thoroughly. Remove oil, grease, and rust. Grind surfaces flat for optimal weld quality. Use jigs to secure leaves. Ensure coaxial alignment error ≤ 0.5 mm. Plan door gap clearance (typically 2–3 mm) to prevent post-weld binding. Gather welding consumables and PPE. Check welder status and gas flow. Confirm welding parameters are set.
Critical Welding Parameters
Use MIG (GMAW) or TIG (GTAW) welding. MIG offers higher speed. TIG delivers finer quality. Control heat input carefully. Use multiple passes and cooling breaks. This minimizes weld stress and distortion. Apply continuous fillet welds. Cover at least 80% of the leaf edge length for strength. Weld sequentially along the hinge axis. Use backstepping or symmetry to manage heat.
Calibration & Adjustment Steps
Calibrate immediately after welding:
- Use a laser level or plumb bob. Align door and frame precisely.
- Ensure uniform height gap and parallelism.
- Check pin hole alignment and pin insertion torque (typically 15–20 N·m). Too tight causes binding; too loose lacks security. Ream holes if necessary.
- Verify smooth door operation. Ensure hinges function flawlessly throughout the full range without binding.
- Double-check all fasteners (pins, screws) are secure.
Post-Weld Processing
- Grind and smooth weld seams.
- Perform stress relief (vibration aging or annealing). Prevent distortion or cracking from residual stresses.
- Apply corrosion protection:
- Carbon steel hinges: Use cold galvanizing or epoxy spray.
- Stainless steel hinges: Apply passivation or oil coating.
- Ensure finished hinge surfaces are burr-free. Keep stainless steel surfaces bright. Prevent damage to door seals and enhance corrosion resistance.
Selection Matrix & Common Mistakes
Key Selection Parameters
- Material: Common options: Zinc-plated carbon steel, 304 Stainless Steel, 316L Stainless Steel. Choose zinc-plated carbon steel for general industry. Opt for 304 or 316L stainless steel in corrosive or explosion-proof settings.
- Load Capacity: Select based on door weight. Include a safety factor of 1.5x or more. Standard ratings include 50kg, 120kg, 200kg+. Consider actual door weight and usage frequency.
- Opening Angle: Standard options: 90°, 110°, 180°. For easier equipment access, choose ≥110° opening.
- Temperature Range: Standard models handle -40°C to 150°C. This suits most indoor/outdoor uses. For high-temp applications (e.g., ovens), select specialized high-temperature hinges rated for 200°C+.
Avoiding Industry Pitfalls
Ignoring Thermal Expansion
Different materials expand differently at high temperatures. Pairing a stainless steel door with carbon steel hinges can cause warping. Match materials closely in high-heat environments.
Overemphasizing Static Load
Don’t just look at rated load. Prioritize fatigue performance under dynamic loads. Ensure hinges pass rigorous cycle testing for frequent operation.
Neglecting Service Access
Install hinges considering future pin removal or inspection. Always leave adequate clearance (min. 50mm front/back) for pin extraction.
Understanding Key Certifications
UL & Fire Ratings
Hinges for fire/safety doors must meet standards like NFPA 80. While hinges may not need UL listing, they must comply with ANSI/BHMA and door manufacturer specs. Ensure reliable function during fire events.
ISO 9001 Quality
Choose manufacturers certified to ISO 9001. This guarantees consistent quality and process improvement.
RoHS Compliance
Hinge materials must meet RoHS directives. They restrict hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, Cr6+). Essential for electrical/electronic equipment.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Create a quarterly hinge inspection checklist:
- Check for loose pins.
- Listen for operational noise.
- Look for rust or coating damage.
- Lubricate pins and bushings annually with high-temp grease. Use silicone oil every 6 months in normal conditions. This reduces wear and prevents sticking.
- Inspect weld areas for cracks. Repair immediately if found.
Fault Tree Analysis Example
Problem: Door Sagging
- Possible Cause 1: Worn hinge bushings or excessive pin/leaf clearance.
- Possible Cause 2: Cracked welds.
Solution: First, check bushing and pin dimensions for excessive wear. Replace bushings or pins if needed. If weld cracks exist, shut down equipment. Perform weld repair and stress relief. If sagging persists, inspect other hinges or supports for looseness.
Standardized Spare Parts Replacement
- Pin Removal Kit: Include dedicated punches/pullers and drip trays for lubricant.
- Bushing Replacement Tool: Use simple press fixtures for new bushing installation.
- Process: Standardize spare parts (pins, bushings) by model. Store them clearly labeled. Maintain detailed replacement logs. After replacement, verify gap clearance and rotation resistance. Ensure performance meets specifications.
Conclusion
Removable pin weld-on hinges transform cabinet door maintenance. Their welded structure delivers unmatched strength and load capacity. The removable pin turns “repairable” into “easily repairable.” This significantly boosts on-site efficiency and slashes total operating costs.
Manufacturers and users must embrace this innovation. Prioritize serviceability right from the design phase. Shift industrial equipment from merely “maintainable” to truly “service-friendly.”
Looking ahead, Industry 4.0 will leverage these hinges. They become platforms for smart maintenance systems. Imagine sensors tracking cycle counts or wear. Enabling predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics. Further enhancing equipment uptime and reliability.


-1-768x768.png)



