HTAN is one of the leading manufacturers of industrial hinges, handles and latches in China.

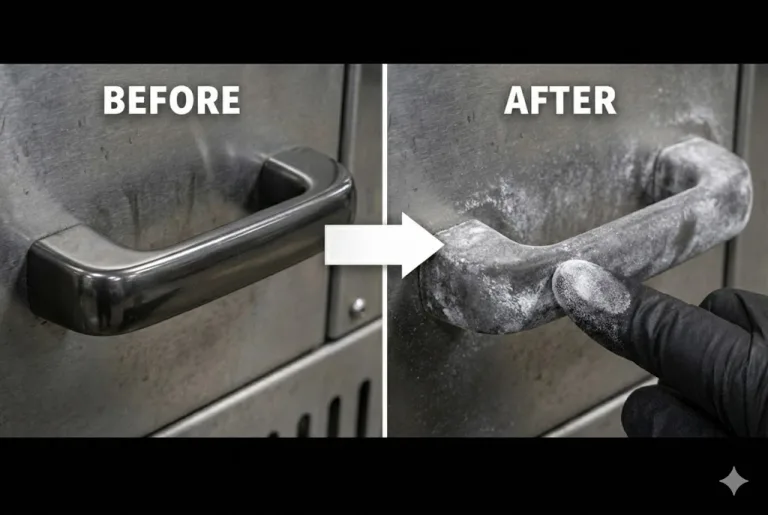
In the outdoor environment, metal equipment will be exposed to moisture, salt, temperature changes and other conditions for a long time, leading to rust or corrosion of the hinges.
Once the hinge fails, the equipment may have poor switching, structural loosening and even safety problems. Therefore, corrosion resistant hinges become a key component to extend the life of outdoor equipment.
In this paper will be from the principle of corrosion, materials and technology to the actual application, detailed analysis of how to choose and maintain corrosion-resistant hinges.
Corrosion mechanism and impact
Environmental factors leading to corrosion
- Humidity: rain or humid air will accelerate metal oxidation, especially iron products are easy to rust.
- Salt: coastal areas or winter salting snow environment, salt will exacerbate the metal surface corrosion
- Temperature changes: thermal expansion and contraction can crack the protective layer on the surface of the hinge, increasing the risk of exposure of the metal inside.
- Chemical contamination: in industrial areas or agricultural fields, acids and alkalis may directly attack the metal.
Hazards of corrosion on hinges
Corrosion can reduce the load-bearing capacity of hinges, leading to jerky rotation, breakage or complete failure.
For example, a rusty hinge may prevent an outdoor door from closing properly or cause the protective cover of an agricultural machine to suddenly fall off.

Materials and technologies for corrosion-resistant hinges
Commonly used corrosion-resistant materials
- Stainless steel (e.g. grade 304/316): contains nickel and chromium, resistant to moisture and salt spray, suitable for coastal or high humidity areas
- Aluminum: lightweight and resistant to oxidation, but needs to be combined with a surface treatment to increase hardness.
- Brass: naturally resistant to corrosion, but more costly, mostly used for high-end outdoor furniture.
- Engineering plastics (e.g. nylon + fiberglass): completely rust-resistant, but with limited load-bearing capacity, suitable for small equipment.
Surface treatment technology
- Powder Coating: Forms a uniform protective layer by electrostatic spraying, color is optional, suitable for outdoor furniture.
- Anodizing (for aluminum): electrolytic process generates an oxide film to enhance hardness and corrosion resistance.
- Galvanizing (e.g. hot dip galvanizing): the zinc layer sacrifices itself to protect the underlying steel, suitable for architectural hardware
Design Optimization
- Sealing structure: Rubber ring or grease grooves are added inside the hinge to block the entry of water.
- Drainage holes: Prevent standing water from remaining and reduce the risk of rusting.
- Non-contact bearings: Use nylon or ceramic bearings to avoid metal friction and rust.

Application Cases
Outdoor Furniture
The hinges of garden doors and patio tables and chairs are often in contact with rainwater, so you need to choose the combination of 304 stainless steel + powder coating, which combines aesthetics and durability.
Marine Equipment
Cabin doors and deck hardware are exposed to salt spray for long periods of time and must use 316 stainless steel or galvanized hinges and pass the ASTM B117 salt spray test.
Agricultural Machinery
Hinges for tractors or irrigation equipment need to resist corrosion from fertilizers and pesticides, with a preference for thick zinc plating or engineering plastics.
Architectural hardware
Outdoor gate hinges for high-rise buildings need to withstand strong wind loads, it is recommended to use stainless steel + anodized reinforced models.

How to choose the right anti-corrosion hinges
Considerations
- Environmental conditions: 316 stainless steel for coastal areas, thick coated steel for industrial areas.
- Load requirements: Stainless steel for load-bearing doors, aluminum or plastic for light equipment.
- Ease of maintenance: Concealed hinges require higher corrosion resistance, exposed hinges require easy lubrication.
Industry Standards and Testing
- Salt spray test : simulate the salt spray environment, test the material corrosion resistance time (e.g., 500 hours without rust)
- Cyclic corrosion testing: alternating salt spray, drying, humidity and heat, closer to real outdoor conditions.
Maintenance and care
Recommendations for longer life
- Clean the hinge surface quarterly with a soft cloth to remove salt or dirt.
- Apply silicone-based grease once a year, avoiding the use of oils that tend to attract dust.
- Check the fixing screws for looseness to prevent the protective layer from wearing out due to vibration.
Common Misconceptions
- Use common stainless steel in acidic environments.
- Neglecting the drainage design, causing water to accumulate inside the hinge.
- Scrubbing the coated surface with steel wire ball damages the anti-corrosion layer.

Conclusion
Anti-corrosion hinge is the core component to ensure the long-term stable operation of outdoor equipment. Through rational selection of materials (e.g. stainless steel, galvanized steel), surface treatment (e.g. powder coating) and regular maintenance (cleaning and lubrication), maintenance costs can be significantly reduced. Whether it’s a ship, agricultural machinery or construction hardware, choosing the right corrosion-resistant hinge for the right environmental conditions can effectively extend the service life of your equipment.
FAQ
Q: How to choose the material according to the environment?
- High salt spray environment (e.g. seaside): 316 stainless steel is preferred.
- Acidic/alkaline environments (e.g. farmland): Choose galvanized steel or chemical-resistant coated hinges.
- Low temperature environment (e.g. North): Avoid engineering plastics with high brittleness.
Q: What is the difference between salt spray testing and cyclic corrosion testing?
- Salt spray test: continuously sprays salt spray and results are more quantifiable
- Cyclic test: simulates the real environment of dry and wet alternation, the cycle is longer
Q: What are the main causes of hinge failure and preventive measures?
- Main causes: materials not resistant to environmental corrosion, lack of lubrication, overloaded use.
- Prevention: Regular inspection, selecting load level according to standard, avoiding violent switching.
Q: How to ensure the performance under extreme temperature?
- Cold environments: Select materials with good low-temperature toughness (e.g., specific stainless steel models).
- High temperature environment: Avoid using plastic bearings and choose metal or ceramic bearings instead.
Q: How can I reduce maintenance costs?
Choose self-lubricating hinges (with built-in grease grooves) or maintenance-free coatings (e.g. Teflon) to reduce the frequency of manual intervention.